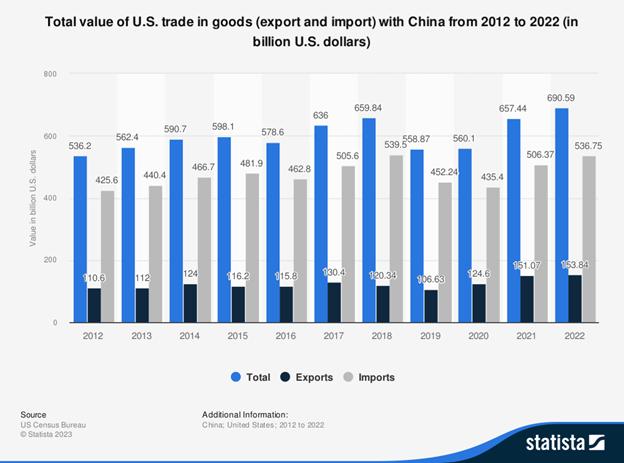
As millions of fathers celebrate Father’s day throughout America on June 18th, the duty of one’s nation will preclude Secretary of State Anthony Blinken, a father of two, from celebrating at home as he arrived in Beijing to manage bilateral relations between the two most important economies of the world. The United States and China are currently in an untenable situation of tension that does not benefit either nation and the stakes could not be higher. Close calls involving military vessels, airplanes, and a lack of collaboration on critical issues such as climate change underscore just a few of the critical transnational issues that have much broader implications. However, one area in which both countries seek to maintain pragmatic relations is on economic matters. While geopolitical tensions have escalated, bilateral trade has continued between the US and China and disruptions can have dire consequences for regional and global economies and supply chains.
Yet a wide gap remains in resolving crucial issues. Moreover, a lack of consistent communication between the upper echelon of the two governments leads to a scarcity of opportunities to improve relations. This leads to the significance of Blinken’s official visit to Beijing. Kurt Campbell, the top Asia expert at the National Security Council said, “intense competition requires intense diplomacy if we’re going to manage tensions.”
Secretary Blinken was initially slated to visit Beijing in February of this year; however, the infamous balloon incident made the trip impossible. This incident involved a Chinese spy balloon discovered over Montana. Regarding the spy balloon, the Pentagon stated it had “very high confidence” that it was sent to gather sensitive information from the U.S. The situation caused an outcry amongst the American public and elected officials, making a trip to China at that time by Secretary Blinken untenable.
Since then, although the U.S. has maintained perceived aggressive economic policies, it has also recognized a necessity to decrease tensions with China. Hence, the change in terminology from selective decoupling to de-risking. Selective decoupling, a process first begun under President Trump, was perceived as a hardline policy questioned by many academics and business moguls alike. Alternatively, de-risking endeavors to portray U.S. efforts of bolstering supply chains less aggressively. The State Department defines de-risking as the “phenomenon of financial institutions terminating or restricting business relationships with clients or categories of clients to avoid, rather than manage, risk.”
Regardless of the change in terminology, Beijing does not see a difference between the two terms. Chinese State media have referred to de-risking as decoupling in disguise. It will be up to Blinken to help clarify the U.S. point of view and decrease tension on this topic. However, there is evidence that China would benefit from an improved economic relationship with the U.S. Recent news that top Chinese VCs are struggling to raise investments underscores this point coupled with the fact that companies need time to recalibrate their strategies after zero covid was abruptly canceled.
Furthermore, U.S. officials have laid the foundation for expanding economic engagement between the two States. This includes Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen, who, in April, called for “constructive” and “healthy” economic relations that benefit both countries. She added that the U.S. does not seek to “decouple” from China and that the U.S. is pursuing healthy economic competition. The business community’s renewed interest in China underscores this idea for potential stabilization in the economic relationship. High-profile business leaders Elon Musk of Tesla
TSLA
On June 18, Secretary Blinken met with top Chinese officials including Chinese Foreign Minister Qin Gang where expectations were set low aiming to primarily stabilize relations. He has scheduled meetings with other senior officials such as Wang Yi, and possibly President Xi Jinping. Although there are issues of concern that Blinken will attempt to address, the economy is a subject that holds significant importance for many. Thus, he will try to reinforce the current thaw in relations and explore areas of cooperation. The top diplomat for East Asia stated that Blinken’s trip to China will focus on “building a floor under the relationship in the name of hopefully imparting some stability to the relationship.” One aspect of this is gaining clarification on a number of critical issues. China has recently passed several new laws that have worried the American business community. The data security law and the counter-espionage law highlight this. There is currently a lack of clarity on what the laws encompass, leading to heightened risks for companies operating in China. Blinken will be tasked with ensuring a favorable business environment for American companies operating in China.
Moreover, Blinken should also encourage the Chinese government to continue communicating with U.S. companies and fostering greater lines of communication. This includes presenting clear red lines that the business community must not cross. This clarification will help provide U.S. businesses with greater reassurance when conducting business in China. In China, US multinationals often view exchanges with regulators in an often paternalistic relationship.
Secretary Blinken may also be forced to address certain issues of concern from the United States’ Congress. Beijing recently banned the purchase of Micron technology chips. The ensuing fallout has led to two Republican-chaired House of Representatives panels—Michael McCaul of the Foreign Affairs Committee and Mike Gallagher of the House Select Committee on the Chinese Communist Party— to state the U.S. must rally allies to defeat Chinese economic coercion. To ensure this issue does not spiral out of control and placate the Republicans in the House, Blinken may seek to address some of these issues.
The visit by Secretary Blinken to Beijing carries significant importance as it presents an opportunity for both sides to clarify their positions, address concerns, and explore areas of cooperation. Ultimately, it is likely that Secretary Blinken’s directive aims to ensure the two countries’ relationship remains on an upward trajectory, and the details of issues are more likely to be discussed at a later date. Engaging in dialogue and seeking common ground aims to build a stable foundation for the U.S.-China relationship, promoting economic cooperation while constructively addressing areas of contention.
Special thanks to Nathaniel Schochet who contributed exceptional content and editorial comments and edits. Special note and thanks to Lorena James for providing pictures and graphs.
Read the full article here